What are Certificate Enrollment Protocols (CEPs)?
Mobile apps such as email, browser, Wi-Fi, and VPN use digital certificates for authentication, digital signatures, and encryption.
CEPs provision and support digital certificates for apps within Samsung devices. This feature enables EMMs and third-party vendors to provide complete certificate enrollment without manual user intervention. Enterprises benefit as IT admins don’t need to issue certificates manually for each device and device users don’t need to authenticate themselves manually.
Enterprises can use CEP to:
- Enroll, renew, or delete certificates, and
- Check your deployment’s certificate enrollment or renewal status
What protocols and standards does CEP support?
KPE extends AE's certificate management APIs by providing this certificate enrollment service API that closely follows the latest security protocols. Therefore, there is no reason to enroll certificates insecurely or implement your own protocols.
The CEP service is very robust, and supports the following frequently used enrollment protocols for provisioning digital certificates:
- Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP): an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) draft used to securely issue certificates to large numbers of network devices using an automatic enrollment technique
- Certificate Management Protocol (CMP): an internet protocol used to manage X.509 digital certificates within a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
- Certificate Management over Cryptographic Message Syntax, Enrollment Over Secure Transport (CMC-EST): describes a simple, yet functional, certificate management protocol targeting PPKI clients that need to acquire client certificates and associated Certification Authority (CA) certificates
You can enable certificate enrollment in the Knox platform using SCEP, CMP, and CMC-EST. For more information on these protocols, see the following resources:
- Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
- SCEP explanations by the IBM Knowledge Centre and Cisco
- CMP explanation by the IBM Knowledge Centre
How does the CEP service asymmetric key cryptography?
Asymmetric key cryptography uses public and private keys to encrypt and decrypt data. The public key is available to all users that use this cryptographic method. The other key—the private key—is a secret key that never leaves the device’s keystore.
An app uses the Samsung Knox CEP service to acquire the public part of the asymmetric key, encrypt a message, and then send the encrypted data to whoever issued the public key. The key owner then applies the private key using the Keystore and decrypts the encrypted information.
How do I install and access the CEP service?
CEP functions within the scope of either the Knox Workspace or personal space, depending on where it is installed.
If the deployment objective is to provision and manage certificates for apps inside the Knox Workspace only, then you must install the CEP services within the Knox Workspace. You can install CEP services within the Knox Workspace as follows:
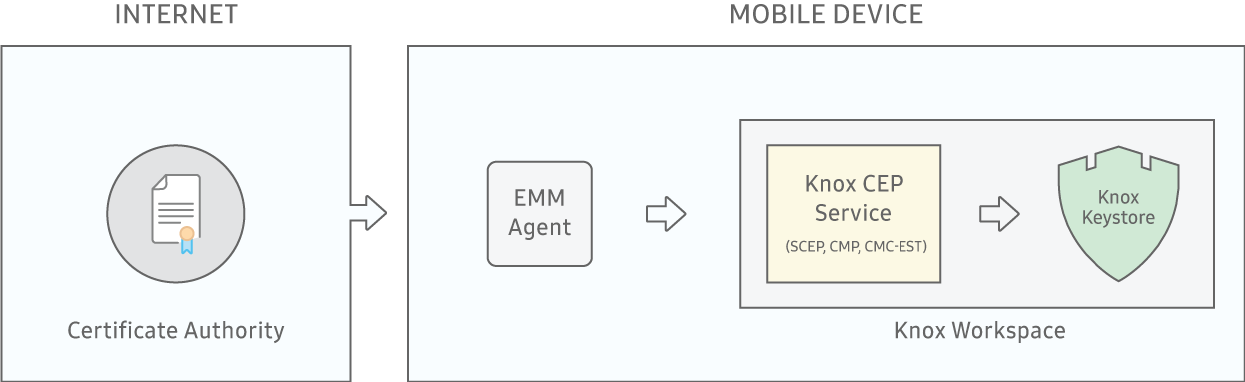
Knox CEP in the Knox Workspace
On the other hand, if the objective is to provision and manage certificates for apps in the personal space, then you can install the CEP services in the personal space.
Flexible and secure, Knox CEP services enable enterprises to configure and automate certificate provisioning to meet their unique needs. The end result? A secure ecosystem allowing only trusted devices to exchange encrypted data, and the protection of corporate assets as well as personal data.
Next steps
To learn more about:
- The advantages offered by Samsung Knox devices over non-Samsung devices, see the KPE Feature Comparison Table.
- Certificate management and other KPE features, see the Knox White Paper.
- How to use the Knox SDK to use the CEP service, read the Knox SDK Developer Guide.
- The benefits of partnering with Samsung, see the Samsung Enterprise Alliance Program.